Resources
Common Questions
You’ll find answers to the most common questions about our PVC conduit, covering everything from specifications to usage. These FAQs are designed to provide quick and helpful information to support your needs.
What is Electrical Conduit?
Electrical conduit refers to the materials utilized to safeguard and maintain the integrity of conducting wires within an electrical system. In addition to promoting organized wiring, conduits play a crucial role in shielding against potential damage that could compromise the connection. They serve as a protective barrier, guarding against threats such as fire, moisture, or chemical vapors. While it is essential for all wiring to be insulated, the use of electrical conduits provides an extra layer of protection, particularly beneficial for cabled or spliced wires.
What Are The Differences Between PVC Pipes and PVC Conduits?
While the manufacturing materials of PVC pipes and PVC conduits are similar, their applications differ across three key dimensions:
- Water Pressure: PVC pipes find utility in pressurized water plumbing systems, whereas PVC conduits are specifically designed for use in electrical systems with wiring.
- Thickness: PVC pipes typically possess greater thickness compared to conduits. The design of PVC conduits doesn’t require extensive thickness since they aren’t subjected to high water pressure. The moderate thickness of PVC conduits aligns with their purpose in electrical systems.
- Waterproofing: PVC pipes are employed in underground or indoor plumbing systems, shielded from sunlight and UV light exposure. Exposure to UV light can be detrimental to PVC pipes. On the other hand, PVC conduits are resilient to sunlight and UV rays, making them suitable for outdoor applications, provided they are waterproof.
What Are Common PVC Conduit Applications?
PVC conduits find widespread use in electrical systems, serving as protective channels for electrical wires and cables. These conduits are suitable for diverse settings, including indoor, underground, and outdoor applications. Whether in residential or commercial environments, PVC conduits prove to be durable, cost-effective, and versatile solutions for safeguarding and organizing electrical wiring.
Are There Installation Considerations With PVC Conduits?
One crucial consideration during conduit installation pertains to bending limitations. A single segment should not exceed 360 degrees of bending without the use of special electrical fittings.
Rigid PVC conduit stands out as a favored conduit type due to its cost-effectiveness and, when equipped with watertight fittings, its suitability for both above and underground applications. While it can be bent, it is more effectively utilized for straight runs.
Is E-Z Weld Conduit by Alva Certified for the US?
Our PVC Conduit is UL Listed SUNLIGHT RESISTANT according to UL 651; in addition, the UL mark appears printed on our product.
Where is the product made?
Our PVC Conduit is manufactured in our plant in Colombia. In addition to PVC conduit, we also manufacture PVC pipe, CPVC, HDPE, and PPR.
What is a bundle, lift or skid?
A bundle is a collection of pvc conduit, tied or wrapped together.
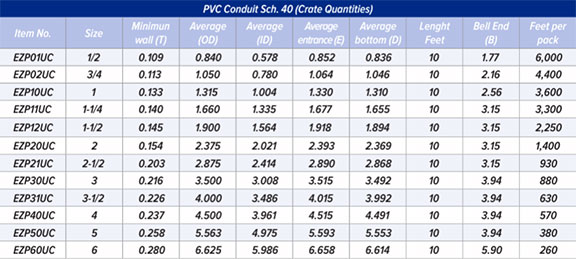
How many feet come in a bundle or pack?
Schedule 40 vs 80 comparison
PVC conduit with SCH 40 and SCH 80 designations refer to two different types of PVC conduit that have different wall thicknesses and are used for different applications.
- Wall Thickness: SCH 40 PVC conduit has a thinner wall compared to SCH 80 PVC conduit. The wall thickness of SCH 40 conduit is generally sufficient for most standard electrical wiring applications, while SCH 80 conduit has a thicker wall, providing increased mechanical strength and durability.
- Mechanical Strength: SCH 80 PVC conduit is typically stronger and more rigid than SCH 40 PVC conduit due to its thicker wall. It is designed to handle heavier loads and is suitable for applications where there may be higher mechanical stress or potential for damage, such as in industrial or commercial settings.
- Durability: SCH 80 PVC conduit is generally more durable than SCH 40 PVC conduit due to its thicker wall, making it more resistant to impact, crushing, and other physical stresses. SCH 80 conduit is often used in applications where increased durability and mechanical protection are required.
- Cost: SCH 40 PVC conduit is typically less expensive than SCH 80 PVC conduit due to its thinner wall. SCH 40 conduit is often used in residential and light commercial applications where cost may be a consideration, while SCH 80 conduit is used in more heavy-duty applications that require increased mechanical strength and durability.
What is the schedule?
The schedule (Sch) is based on the wall caliper or “thickness” of a pipe. Two pipes of the same diameter may have different schedules, which means they have a different wall thicknesses.
Electrical conduit warranty
All our PVC conduits have a 1-year warranty. Please refer to our resource section in our website to access the warranty.
Where should you use Schedule 80 PVC Conduit?
SCH 80 PVC conduit is typically used in more demanding applications, such as industrial, commercial, outdoor, and underground installations, where increased mechanical strength and durability are required.
What associations are we part of?
- NAED (National Association of Electrical Distributors).
- NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association).
- NEMRA (National Electrical Manufacturers Representative Association).
What are the advantages of PVC electrical conduit over metal conduit?
- Corrosion Resistance: Non-metallic conduit is resistant to corrosion, which makes it ideal for use in outdoor and damp environments. In contrast, metal conduit can corrode over time, particularly if it is exposed to moisture or other harsh conditions.
- Lightweight and Easy to Install: Non-metallic conduit is much lighter than metal conduit, which makes it easier to install and handle. This can result in faster installation times and lower labor costs.
- Low Conductivity: Non-metallic conduit has low conductivity, which means that it doesn’t conduct electricity. This can be an advantage in situations where you want to reduce the risk of electrical shock.
- Cost-effective: Non-metallic conduit is generally less expensive than metal conduit, making it an attractive option for projects with tight budgets.
- Chemical Resistance: Non-metallic conduit is resistant to many chemicals and solvents, which can make it a good choice for use in industrial or chemical applications.
Need Assistance?
We are here to help!
Our team is ready to help you with all the details
Ready to Order?
Ready to order or need help with a product? Our team is ready to help you with all the details
